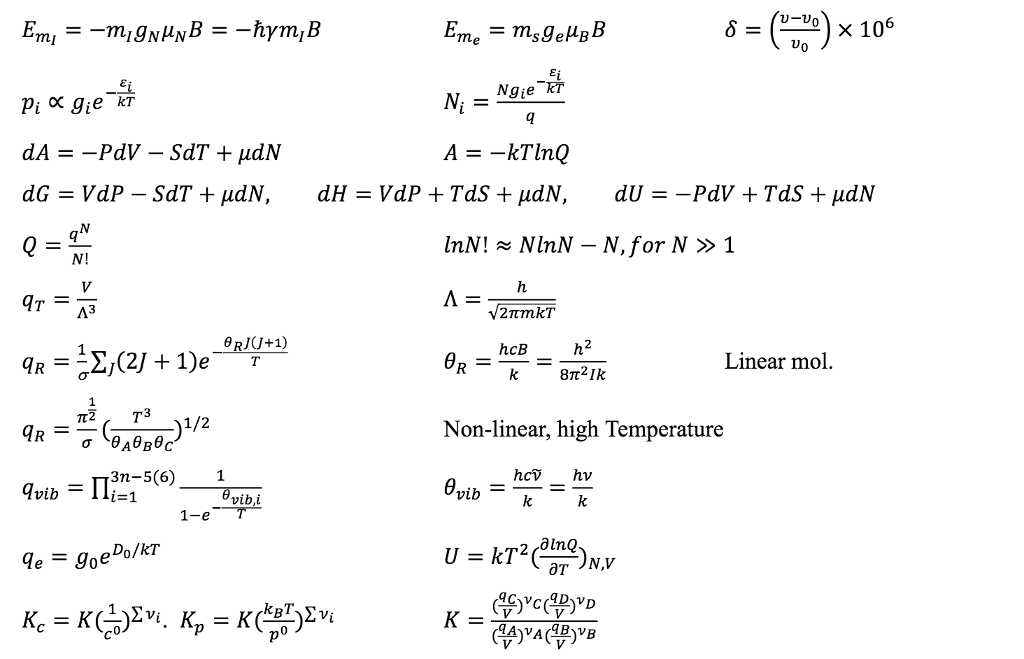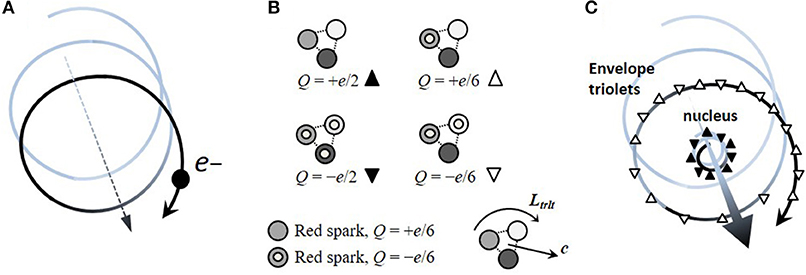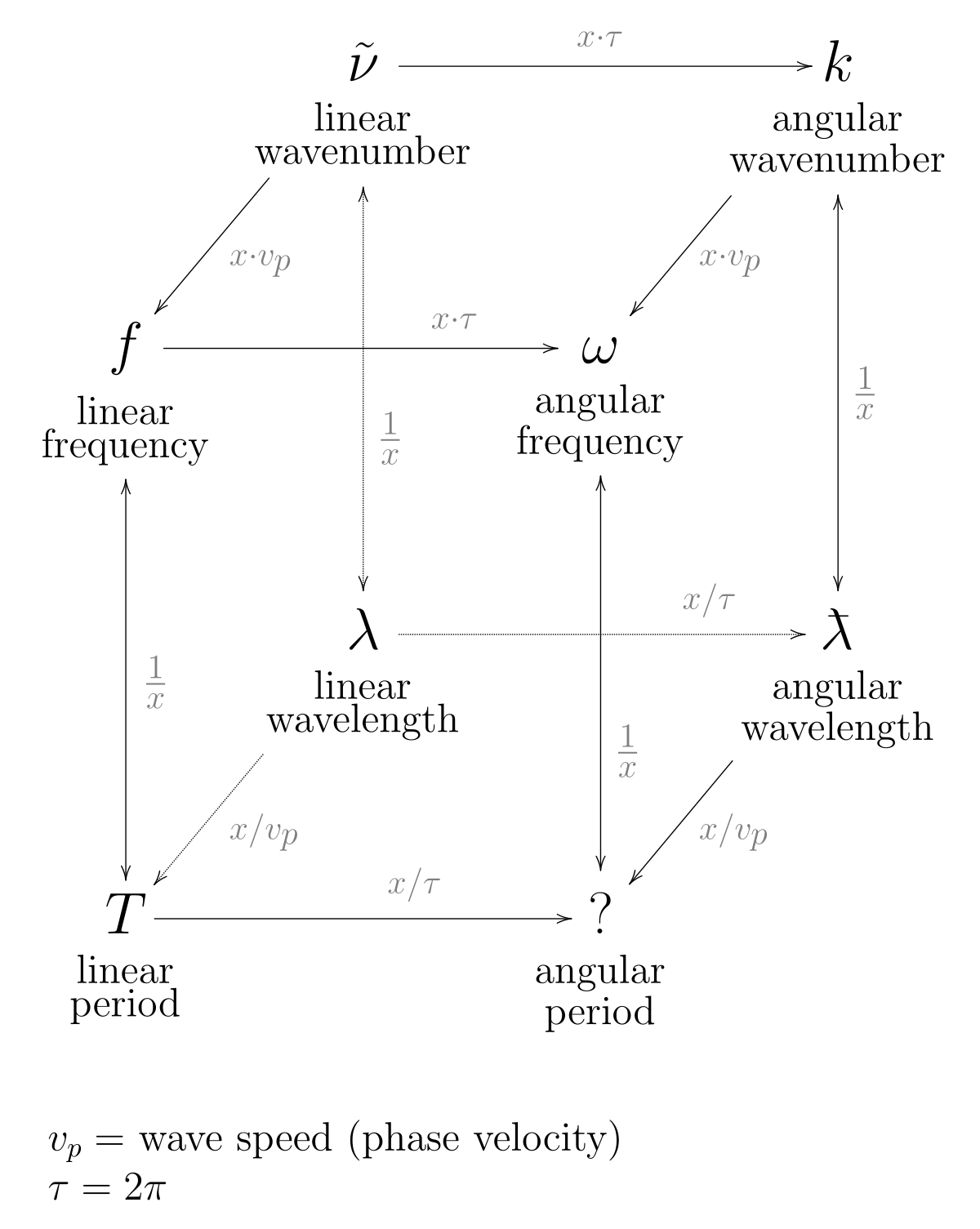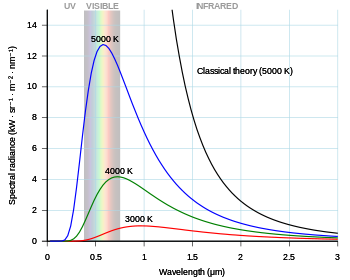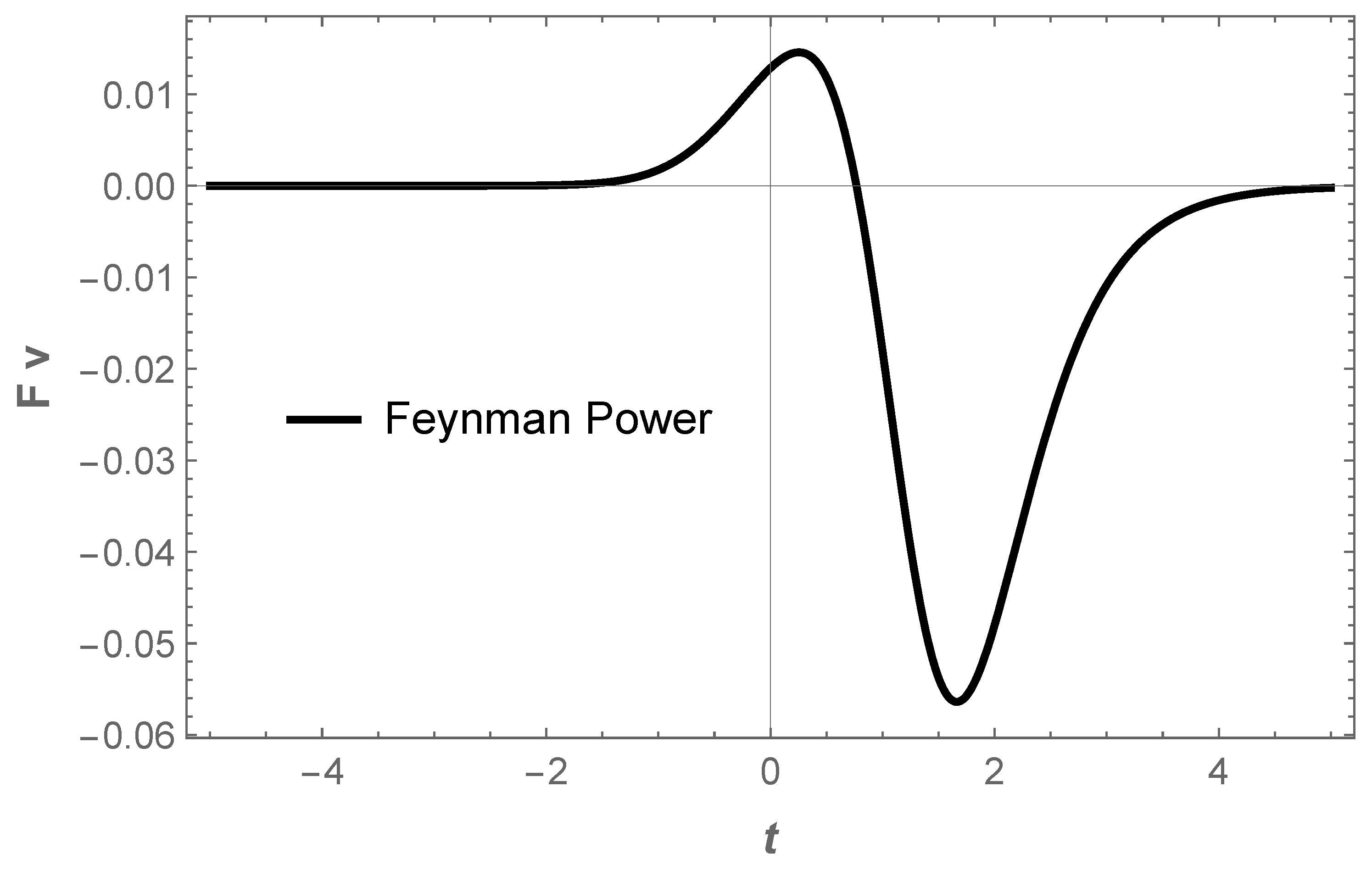
Physics | Free Full-Text | Electron as a Tiny Mirror: Radiation from a Worldline with Asymptotic Inertia

Antioxidants | Free Full-Text | The Influence of 5′,8-Cyclo-2′-Deoxyguanosine on ds-DNA Charge Transfer Depends on Its Diastereomeric Form: A Theoretical Study

What will be the uncertainty in velocity of an electron when the uncertainty in its position is 1000 A ?

SOLVED: Constants: Boltzmann constant k = 1.38x10-2 JK OR 8.61x10 'eV/K Electron charge e =-E6x[0 19 € Free electron mass m = 9.1xlO "kg Plank constant h = 6.6x105+ J.s Reduced Planck's

For a two dimensional particle in a box and we have this molecule, with 26 pi electrons, what should the n's be in the Schrodinger equation? In other words, which orbitals are
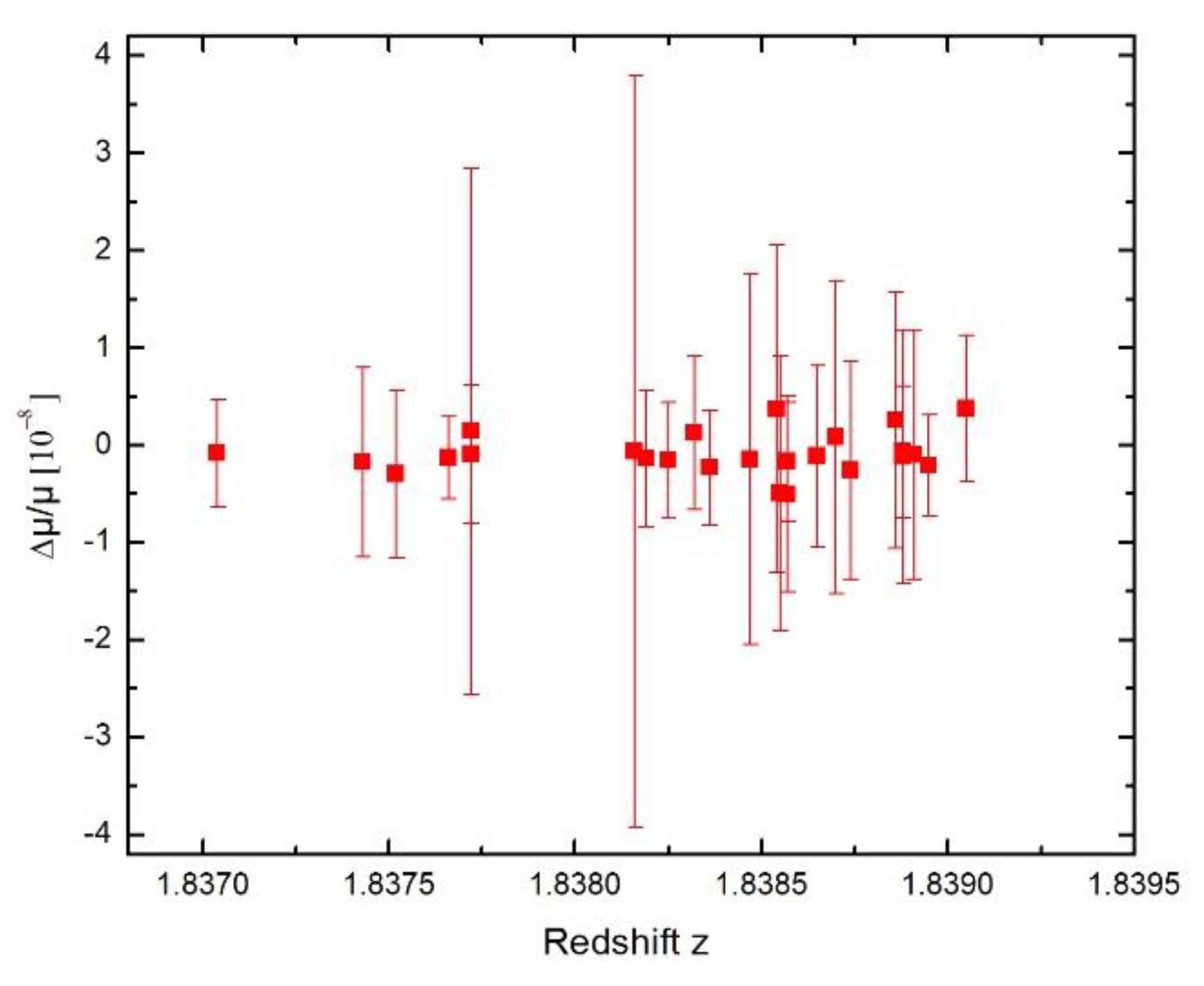
Symmetry | Free Full-Text | New Limit on Space-Time Variations in the Proton-to-Electron Mass Ratio from Analysis of Quasar J110325-264515 Spectra
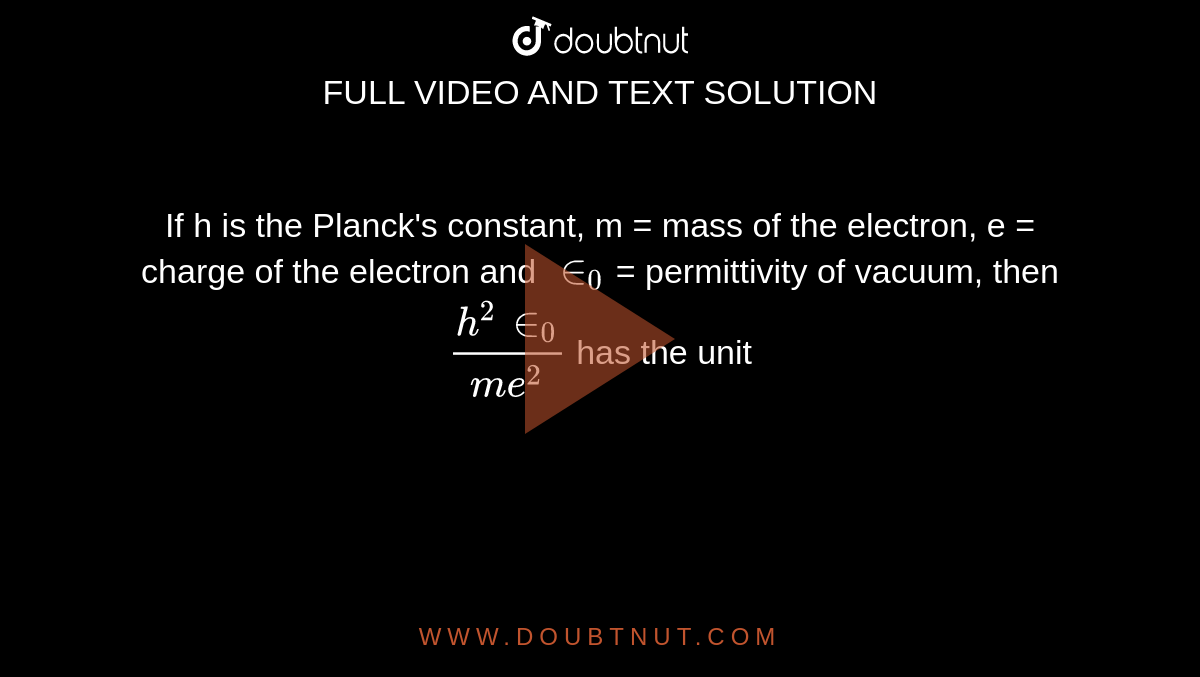
If h is the Planck's constant, m = mass of the electron, e = charge of the electron and in(0) = permittivity of vacuum, then (h^(2)in(0))/(me^(2)) has the unit

If h is the Planck's constant, m = mass of the electron, e = charge of the electron and in(0) = permittivity of vacuum, then (h^(2)in(0))/(me^(2)) has the unit

SOLVED: Data Sheet Speed of light =3X108 m -1 Planck's constant h = 6.626 X 10-34 J s Planck's constant, reduced h= h/2n 1.055 X 10-34 Js 6.582 x 10- 22 MeV